Low float stocks refer to shares of a company that are available for trading in the open market and are not held by institutional investors, insiders, or other long-term holders. The term “float” represents the number of outstanding shares that can be freely bought and sold by the public. Low float stocks are characterized by a relatively small number of shares in the market, which can lead to higher volatility and price fluctuations. Investors often find these stocks appealing due to the potential for rapid price movements, but they also pose increased risks. A comprehensive guide to understanding low float stocks involves exploring their characteristics, factors influencing their prices, trading strategies, and risk management techniques. By delving into the nuances of low float stocks, investors can gain insights into this unique segment of the market and make informed decisions to navigate its challenges effectively and potentially make quick profits.
Low Float Stocks Explained
Low float stocks are shares of a company that have a relatively small number available for trading in the open market. The term “float” refers to the total number of shares outstanding that are not held by insiders, institutional investors, or other long-term stakeholders as opposed to authorized shares which is the maximum number of shares that a company is legally allowed to issue. The number of authorized shares is specified in the corporate charter or articles of incorporation. The stock float represents the actual shares available for the investors to buy and sell on the stock market. One key metric associated with shares float is the percent of float. Traders are interested in knowing the float ratio because it provides valuable insights into the liquidity and potential price volatility of a stock. The formula for percent of float is:
Percent of Float = ( Number of shares in Float / Total Outstanding Shares ) x 100
In the context of low float stocks, this means there is a limited supply of shares available for public trading. The scarcity of shares can lead to increased volatility in the stock’s price, as even a small number of buy or sell orders can have a significant impact.
Investors are often attracted to low float stocks because of the potential for rapid price movements, which can result in substantial and quick profits. However, it’s important to note that the same volatility also introduces higher degree of risk, and prices can experience sharp declines just as quickly as they rise. Trading low float stocks requires careful consideration of market conditions, timing, and risk management strategies to navigate the unique challenges associated with these stocks.
Benefits of Trading Stocks From a Company With Low Float
Trading shares of stocks from a company with a low float can present unique opportunities and benefits for investors willing to navigate the associated risks. One primary advantage is the potential for heightened volatility. With a limited number of shares available in the open market, any significant buying or selling activity can lead to rapid price movements. For traders adept at reading market trends and making quick decisions, this volatility can translate into substantial short-term gains. The relatively small supply of shares also means that positive news or developments can trigger a surge in demand, potentially driving the stock price higher.
Furthermore, low float stocks may be more responsive to specific catalysts. News, earnings reports, or other fundamental developments can have a pronounced impact on stocks with a low float, as there is less liquidity in the market. This responsiveness provides traders with the opportunity to capitalize on short-term events, allowing for potentially lucrative trades based on timely and accurate information.
Additionally, the potential for quick and significant price movements in low float stocks can attract attention from momentum traders and speculators. This increased interest can create a dynamic trading environment, fostering liquidity and trading opportunities. Traders who thrive in fast-paced markets may find low float stocks to be particularly appealing due to the potential for rapid price changes.
Despite these benefits, it’s crucial for investors to approach trading low float stocks with caution. The same volatility that can lead to quick profits also exposes traders to higher risks, including the potential for sharp and unpredictable price declines. Adequate risk management strategies, thorough research, and a disciplined approach are essential for those looking to capitalize on the benefits of trading stocks from companies with low float. Overall, while low float stocks offer unique opportunities, they require a careful and informed approach to navigate successfully.
Risk of Trading Stocks From a Company With Low Float
Trading stocks from a company with a low float comes with a set of inherent risks that investors must carefully consider before engaging in such markets. One of the primary challenges is the heightened volatility associated with low float stocks. Due to the limited number of shares available for trading, these stocks are more susceptible to rapid price movements triggered by relatively small trades. While this volatility presents opportunities for quick profits, it also amplifies the potential for significant losses, as prices can plummet just as swiftly as they rise.
The liquidity risk is another crucial factor to bear in mind when trading low float stocks. With fewer stock shares available, the market for these stocks may lack the depth and breadth seen in more liquid securities. This can result in wider bid-ask spreads and increased difficulty executing trades at desired prices. In times of market stress or heightened uncertainty, low float stocks may experience a lack of buyers or sellers, exacerbating liquidity challenges and making it harder for investors to exit positions at favorable terms.
Moreover, low float stocks are often more susceptible to manipulation. The limited supply of shares makes it easier for a relatively small number of trades to influence the stock price. This susceptibility to market manipulation can expose traders to fraudulent activities, pump-and-dump schemes, or other manipulative practices that can lead to substantial financial losses.
Additionally, the lack of analyst coverage and institutional interest in low float stocks can contribute to information asymmetry. Investors may have limited access to reliable information about the company’s fundamentals, making it challenging to make well-informed investment decisions. The absence of institutional support may also lead to wider price fluctuations, as large institutional trades can have a stabilizing effect on more widely held stocks.
While trading stocks from companies with low float can offer opportunities for quick profits, it is crucial for investors to acknowledge and mitigate the substantial risks involved. A thorough understanding of the market dynamics, diligent research, disciplined risk management, and a cautious approach are essential for navigating the challenges associated with low float stocks and preserving capital in this high-risk trading environment.
3 Key Factors You Need To Consider When Trading
When making the investment decision to trading low float stocks, three key factors take on particular significance due to the unique characteristics of these securities. First and foremost, volatility is a crucial consideration. Low float stocks are prone to rapid and substantial price movements, driven by the limited number of shares available for trading. Traders must be prepared for heightened volatility and the potential for sharp price fluctuations, necessitating robust risk management strategies and must also recognize the period of time for low stock trading can vary.
Liquidity is another critical factor when trading low float stocks. With fewer shares available in the market, these stocks may experience thinner trading volumes, leading to wider bid-ask spreads and challenges in executing trades at desired prices. Traders should carefully assess liquidity conditions to ensure they can enter and exit positions effectively, minimizing the impact of slippage.
Additionally, due diligence and information asymmetry play a pivotal role. Low-float company stocks often lack comprehensive analyst coverage and institutional interest unlike high-float stocks, making it challenging to access reliable information about the companies. Traders need to conduct thorough research, scrutinize financial reports including the balance sheet, and stay informed about any relevant news or developments. Being aware of the information gaps and uncertainties associated with low float stocks is crucial for making informed trading decisions and managing risks effectively in this dynamic market segment.
1. High Volume in the Stock Market
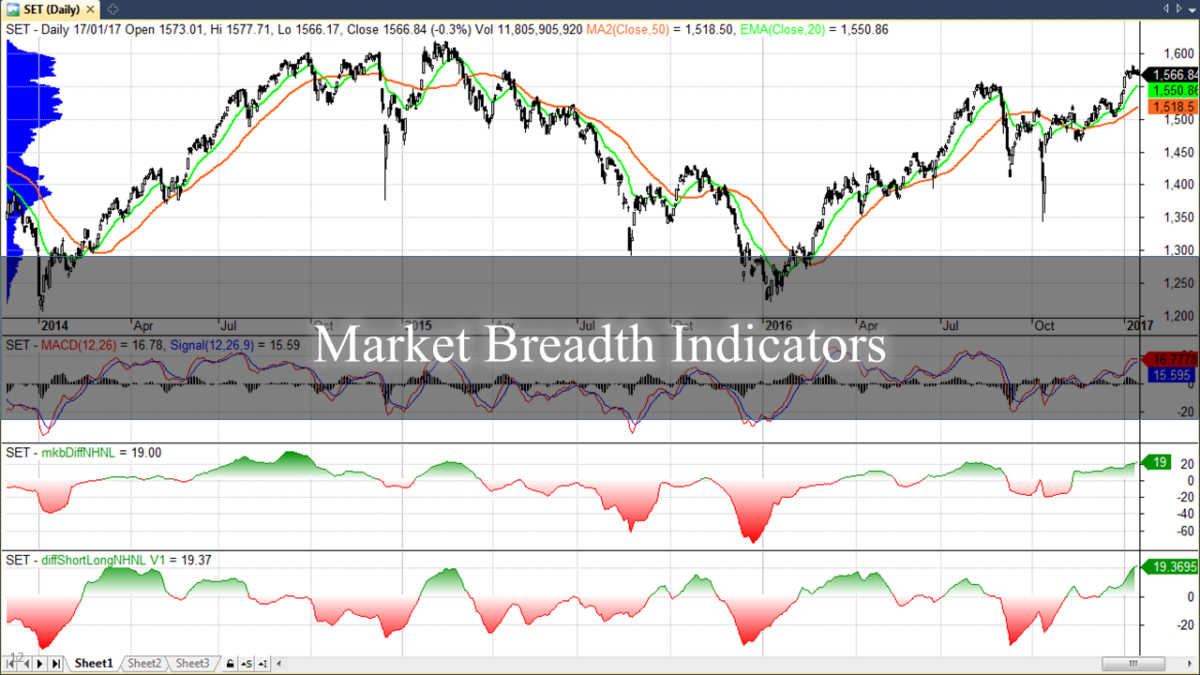
High volume in the stock market, particularly when trading low float stocks, is a critical factor that demands careful consideration. Elevated trading volumes in stocks with low float can signify increased investor interest and participation, potentially leading to greater liquidity and smoother execution of trades. However, it’s essential to recognize that high volume in low float stocks can also exacerbate volatility. With a limited number of shares available, a surge in buying or selling activity can result in rapid and exaggerated price movements. Traders should monitor volume trends closely, as it provides insights into market dynamics and can indicate the strength or weakness of a price trend. Successful navigation of high volume scenarios in small float stocks requires a keen understanding of market psychology, risk management, and the ability to interpret volume patterns to make well-informed trading decisions.
2. News Catalysts
News catalysts play a pivotal role in the dynamics of trading low float stocks, significantly influencing price movements and overall market sentiment. Due to the limited number of shares available for trading, low float stocks are particularly responsive to news events, as even a small influx of buying or selling activity can lead to pronounced price swings. Traders actively monitor news catalysts such as earnings reports, product launches, regulatory developments, or industry trends, as these can act as powerful triggers for volatility. Positive news can result in a surge of demand, rapidly driving up prices, while negative or bad news can lead to a swift sell-off. It’s crucial for traders to stay vigilant, react quickly to relevant news, and integrate comprehensive research into their trading strategy. The ability to anticipate and respond effectively to news catalysts is essential for those navigating the dynamic landscape of low float stocks, where timely information can significantly impact trading outcomes.
3. Float Percentage
The float percentage is a critical metric to consider when trading low float stocks, as it directly influences the stock’s liquidity and price dynamics. The float percentage represents the proportion of a company’s outstanding shares that are available for public trading. In the context of low float stocks, where the number of tradable shares is limited, the float percentage is often significantly lower than in stocks with larger floats. This scarcity of available shares amplifies the impact of buying or selling activity on the stock’s price. Traders closely monitor the float percentage to gauge the potential for volatility, as a lower float percentage can result in more pronounced and rapid price movements. Additionally, understanding the float percentage helps traders assess the risk and reward profile of low float stocks, informing their decision-making process and risk management strategies in this inherently dynamic and volatile segment of the market.
Hit Your Profit Targets by Day Trading Low Float Stocks
Achieving profit targets through day trading low float stocks requires a strategic approach and utilizing tools like “Above the Green Line” can be instrumental in guiding traders. Low float stocks are known for their volatility, presenting both opportunities and risks. To hit profit targets, traders need to capitalize on price fluctuations within a single trading day. “Above the Green Line” refers to a technical analysis tool commonly used to identify upward trends and potential entry or exit points. The benefits of incorporating this tool into day trading low float stocks include its ability to provide a visual representation of price trends and support decision-making based on market momentum.
Above the Green Line assists traders in identifying key levels where stocks are more likely to experience a breakout or a breakdown. This is crucial for day traders aiming to enter positions at optimal points and secure profits quickly. The tool can also help in setting stop-loss orders and managing risks effectively by signaling potential reversals or trend continuations. Its visual nature simplifies the process of recognizing patterns and trends in low float stocks, enabling traders to make timely and informed decisions.
Moreover, Above the Green Line aids in establishing realistic profit targets. By analyzing historical price movements and trends, traders can set achievable goals for each trade. This tool enhances the precision of identifying entry and exit points, aligning with a trader’s profit targets and risk tolerance. Consistently hitting profit targets in day trading low float stocks requires a disciplined approach, and Above the Green Line serves as a valuable guide for traders seeking to navigate the volatile nature of this market successfully.
For those interested in learning more about trading low float stocks and how it may be incorporated into your portfolio whether directly or indirectly, we invite you to join Above The Greenline.