Dow 30

What is the Dow 30?
The Dow 30, also known as the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DIJA), is an index that was developed in 1896 to track the overall health of the stock market. Founded by Charles Dow and his business partner Edward Jones, the Dow 30 made waves by establishing itself as one of the first indices to track market health during an era of limited information. The Dow’s long history of success has made it a benchmark for many investors. So much so that when reporters refer to the market as “being up today”, they mean that the Dow is up.
How Does the Dow 30 Work?
In its early stages, the DIJA consisted of 12 companies that were considered impactful to the United States’ economy. Today, the Dow 30 works by combining the price of the 30 largest publicly traded companies and dividing the sum by a certain number. The Dow Divisor changes every now and then depending on stock splits and stock dividends. Thus, the Dow 30 provides an analysis of overall market health while simultaneously accounting for changes. Furthermore, the Dow 30 regularly makes changes to the composition of the index when companies become less relevant or do not reflect the current trends of the economy. The weight each company has within the index depends on its share price. Stocks with higher share prices will have a larger weight within the index and thus have a greater capacity to change the index’s value. If investors so choose, they can purchase shares of the Dow which would allow them access to all 30 companies listed within the index.
Companies Within the Dow 30
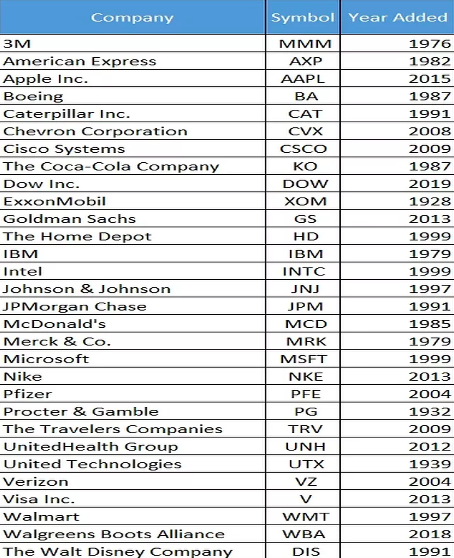
The Dow 30 includes a variety of corporations; however, they can all be generally described as “blue-chip companies”. Blue-chip companies tend to have national reputations for quality, stability, and profitability. As previously mentioned, depending on the economic condition, companies are regularly taken out and added by a committee that has employees from The Wall Street Journal and the S&P Dow Jones Indices. The list of corporations within the Dow 30 has changed 60 times since 1928. Below is an alphabetical list of companies within the index as of May 2020.
Risk of the Dow 30
There are a number of critics who believe that the Dow 30 does not fully represent the condition of the U.S. economy as it only contains 30 corporations. Critics believe the composition of the index is too small and thus fails to consider companies of different sizes and industries. These critics tend to favor the S&P 500 as they believe it has a more comprehensive list of companies that can better understand the state of the market. Additionally, the S&P 500 tracks and factors in market capitalization. Market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the number of outstanding shares times the market price. The Dow 30 does not represent the market capitalization of its companies. As such, critics tend to also believe that simply accounting for share price does not provide an accurate examination of market health and tend to favor indices that utilize market capitalization.
Conclusion
The Dow 30 is a landmark index that has been around for over a century. It has reached many historical milestones from its foundation in a limited information era to large percentage gains. The Dow 30 has long functioned as a way for investors and economic analysts to gauge the overall health of the market. While it does not contain nearly as many corporations as the S&P 500, there is something to be said for its great historical success and ability to advance for so many years.