Understanding the Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Report
The Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Report is a key economic indicator published monthly by the Federal Reserve. This report provides valuable insights into the performance of the industrial sector of the economy, including manufacturing, mining, and utilities. It reflects how effectively industries are utilizing their production capacity and serves as an essential tool for understanding economic growth and investment opportunities.
Key Components of the Report
- Industrial Production Index: This index measures the output of the industrial sector, providing a comprehensive overview of production trends. It includes data from manufacturing, mining, and utilities, helping analysts assess overall industrial activity.
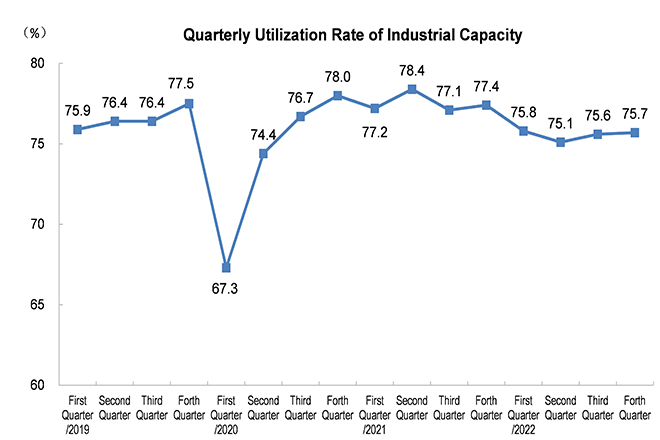
- Capacity Utilization Rate: This metric indicates the percentage of potential output that is actually being realized in the industrial sector. A high utilization rate suggests strong demand and efficient production, while a low rate may indicate excess capacity or weakening demand.
- Sector Breakdown: The report breaks down industrial production by sector, allowing for detailed analysis of trends within manufacturing, mining, and utilities. This segmentation helps investors identify which areas are performing well and which may be struggling.
- Comparative Analysis: The report provides comparisons of current data to historical figures, enabling analysts to identify trends over time and assess the overall health of the industrial sector.
Impact on the Investment Community
The Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Report has a significant impact on the investment community for several reasons:
1. Economic Health Indicator
Industrial production is closely linked to overall economic health. Rising production levels generally signal economic expansion, while declining production can indicate a slowdown. Investors closely monitor this data to gauge economic conditions and adjust their portfolios accordingly.
2. Sector Investment Decisions
Different sectors of the industrial economy respond variably to production data. For example, strong manufacturing output may benefit industrial stocks and sectors related to construction and raw materials. Conversely, weak production figures may prompt investors to reevaluate their exposure to cyclical sectors, potentially shifting focus to defensive industries.
3. Monetary Policy Implications
The report can influence monetary policy decisions made by the Federal Reserve. Strong industrial production data may lead to expectations of tighter monetary policy to combat inflation, while weak production may prompt the Fed to maintain or lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity.
4. Stock Market Reactions
The stock market often reacts to changes in industrial production. Positive data may lead to gains in industrial and manufacturing stocks, while disappointing figures can result in declines. Investors use this information to make timely trading decisions.
5. Bond and Currency Markets
Industrial production data can affect bond yields and currency values. Strong production may lead to rising bond yields as investors anticipate inflation and interest rate hikes. Conversely, weak production data can lead to lower yields as investors seek safety in bonds. In currency markets, strong industrial output can strengthen the dollar, while weak data may lead to depreciation.
Insights from the Report
- Supply Chain and Demand Insights: The report provides insights into supply chain dynamics and demand trends. An increase in industrial production can indicate rising consumer demand, while a decrease may signal shifts in purchasing patterns.
- Capacity Constraints: Analyzing capacity utilization helps investors understand potential constraints in production. High utilization rates may indicate supply bottlenecks, leading to potential price increases for goods and services.
- Regional Variations: The report often highlights regional production trends, allowing analysts to identify areas of strength or weakness. This regional analysis can inform investment strategies targeting specific markets or sectors.
- Impact on Employment: The industrial sector is a significant source of employment. Changes in production levels can directly impact hiring and job creation. Investors often look at employment trends in conjunction with production data to gauge overall economic health.
Economic Cycles and Industrial Production
The Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Report is integral to understanding economic cycles:
- Expansion: During periods of economic expansion, industrial production typically increases as demand rises. Investors often focus on growth-oriented stocks during these times, anticipating rising corporate profits.
- Peak: At the peak of the economic cycle, production may stabilize as demand levels off. Investors may begin to diversify their portfolios in anticipation of a potential downturn.
- Contraction: In times of economic contraction, industrial production often declines as companies reduce output in response to falling demand. Investors may shift towards defensive stocks and sectors that are less sensitive to economic fluctuations.
- Trough: At the trough of the cycle, production may stabilize or begin to recover, indicating potential economic recovery. Investors often look for undervalued assets during this phase, anticipating future growth as conditions improve.
Conclusion
The Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Report is a vital economic indicator that provides essential insights into the health of the industrial sector and the overall economy. By analyzing production and utilization data, investors can make informed decisions about asset allocation, sector exposure, and risk management. As a key gauge of economic performance, the report shapes market sentiment and influences various financial markets, making it essential for investors to closely monitor its implications.

