CBOE Volatility Index (VIX)
Created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), the Volatility Index, or VIX, is a real-time market index that represents the market’s expectation of 30-day forward-looking volatility. Derived from the price inputs of the S&P 500 index options, it provides a measure of market risk and investors’ sentiments. It is also known by other names like “Fear Gauge” or “Fear Index.” Analysts, portfolio managers and Investors look to VIX values as a way to measure market risk, fear and stress before they take investment decisions.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The CBOE Volatility Index, or VIX, is a real-time market index representing the market’s expectations for volatility over the coming 30 days.
- Investors use the VIX to measure the level of risk, fear, or stress in the market when making investment decisions.
- Traders can also trade the VIX using a variety of options and exchange-traded products, or use VIX values to price derivatives.
How is Volatility Measured
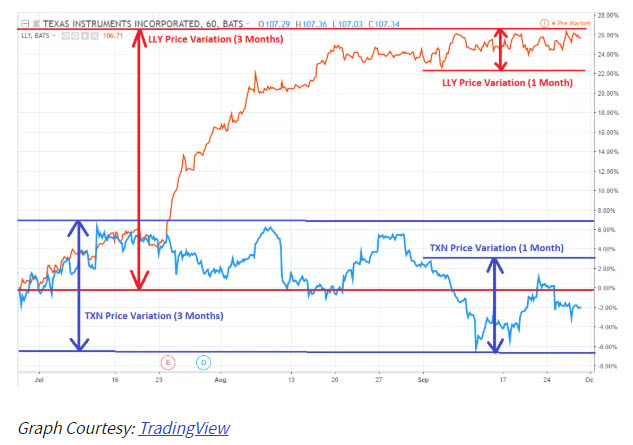
There are two different methods for calculating market volatility. First is based on performing statistical calculations on the historical prices over a specific time period; or the second method to measure volatility involves inferring its value as implied by option prices. Options are derivative instruments whose price depends upon the probability of a particular stock’s current price moving enough to reach a particular level (called the strike price or exercise price).
FINAL COMMENTS
Volatility indices are sentiment indicators that react to stock market movements. They are NOT predictors but highlight sentiment extremes. As with other sentiment indicators, the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX) should ONLY be used in conjunction with other indicators for market timing.